
暂无数据~
Tricyclic antidepressants block cholinergic nicotinic receptors and ATP secretion in bovine chromaffin cells 
Abstract Nicotine-induced ATP secretion from chromaffin cells was blocked by imipramine and desipramine. This blocking action took place on both, fast and slow, components of ATP secretion. Exposure of chromaffin cells to nicotine (10 μM) for 4 s induced an inward current of about −155 pA. Imipramine and desipramine blocked, in a concentration-dependent manner, both peak inward current and total charge influx in response to nicotine. In addition, imipramine and desipramine partially (40%) blocked depolarization-induced ATP secretion and Ca2+ currents evoked by high K+. This suggests that tricyclic antidepressants block nicotine-induced ATP secretion by acting on two targets: one is the nicotinic receptor itself and the second one are voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels.

Augmentation of retinoic acid-induced granulocytic differentiation in HL-60 leukemia cells by serine/threonine protein phosphatase inhibitors 
Abstract To evaluate the involvement of protein phosphatases (PP) in differentiation of human myclogenous leukemia HL-60 cells, we made use of potent inhibitors of PP1 and PP2A, calyculin-A (CAL-A) and okadaic acid (OKA). CAL-A and OKA could augment all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced granulocytic differentiation, whereas the differentiation toward macrophage lineage by 12-o-tetradecanoylphorbol acetate (TPA) was unchanged in the presence of CAL-A. CAL-A augmented the phosphorylation or 18K, 23K and 30K proteins induced by ATRA. The PP1 and PP2A were identified and were present mainly in the cytosol of HL-60 cells. These results suggest that either PP1 or PP2A or both may be involved in regulating granulocytic differentiation or HL-60 cells.

Pan-Genotype Hepatitis E Virus Replication in Stem Cell–Derived Hepatocellular Systems 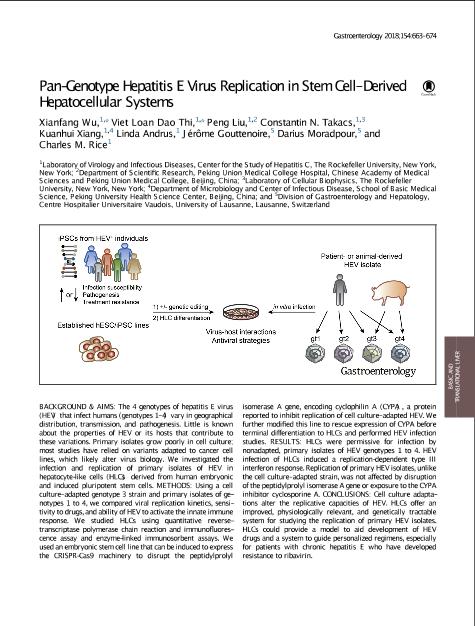
Background & Aims The 4 genotypes of hepatitis E virus (HEV) that infect humans (genotypes 1–4) vary in geographical distribution, transmission, and pathogenesis. Little is known about the properties of HEV or its hosts that contribute to these variations. Primary isolates grow poorly in cell culture; most studies have relied on variants adapted to cancer cell lines, which likely alter virus biology. We investigated the infection and replication of primary isolates of HEV in hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs) derived from human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Methods Using a cell culture–adapted genotype 3 strain and primary isolates of genotypes 1 to 4, we compared viral replication kinetics, sensitivity to drugs, and ability of HEV to activate the innate immune response. We studied HLCs using quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence assay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. We used an embryonic stem cell line that can be induced to express the CRISPR-Cas9 machinery to disrupt the peptidylprolyl isomerase A gene, encoding cyclophilin A (CYPA), a protein reported to inhibit replication of cell culture–adapted HEV. We further modified this line to rescue expression of CYPA before terminal differentiation to HLCs and performed HEV infection studies. Results HLCs were permissive for infection by nonadapted, primary isolates of HEV genotypes 1 to 4. HEV infection of HLCs induced a replication-dependent type III interferon response. Replication of primary HEV isolates, unlike the cell culture–adapted strain, was not affected by disruption of the peptidylprolyl isomerase A gene or exposure to the CYPA inhibitor cyclosporine A. Conclusions Cell culture adaptations alter the replicative capacities of HEV. HLCs offer an improved, physiologically relevant, and genetically tractable system for studying the replication of primary HEV isolates. HLCs could provide a model to aid development of HEV drugs and a system to guide personalized regimens, especially for patients with chronic hepatitis E who have developed resistance to ribavirin.

Anionic Lipids Modulate the Activity of the Aquaglyceroporin GlpF 
Abstract The structure and composition of a biological membrane can severely influence the activity of membrane-embedded proteins. Here, we show that the E. coli aquaglyceroporin GlpF has only little activity in lipid bilayers formed from native E. coli lipids. Thus, at first glance, GlpF appears to not be optimized for its natural membrane environment. In fact, we found that GlpF activity was severely affected by negatively charged lipids regardless of the exact chemical nature of the lipid headgroup, whereas GlpF was not sensitive to changes in the lateral membrane pressure. These observations illustrate a potential mechanism by which the activity of an α-helical membrane protein is modulated by the negative charge density around the protein.

Changeable Conditional Survival Rates and Associated Prognosticators in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Receiving First Line Targeted Therapy 
Purpose In this study we evaluated conditional survival probabilities in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who underwent first line tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. We also identified identify predictors of conditional survival with time. Materials and Methods We retrospectively reviewed clinical data on 1,659 individuals with metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the Korean Renal Cancer Study Group database, of whom the records of 1,131 were finally analyzed. The primary end point was conditional overall survival. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to calculate conditional overall survival probabilities using the formula, conditional survival (α│β) = S(α + β)/S(β), indicating the likelihood of additional α years survivorship in person who has already survived for β years after initial therapy. S(χ) represents the actual survival rate. Multivariate Cox regression model was used to identify predictors of conditional survival with time. Results Six, 12, 18, 24 and 36-month conditional overall survival gradually increased in patients at all additional survival times after initial treatment compared to patient baseline survival estimations. While the actual overall survival rate decreased with time, the 36-month conditional overall survival rate was calculated as 7.3% higher in patients who had already survived 36 months compared to baseline estimations at the time of initial tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. Furthermore, predictors of conditional overall survival changed with time. Only previous metastasectomy remained a key prognosticator of conditional overall survival until 36 months of survival following initial tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. Conclusions Conditional survival improved with time after initial tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Our study offers valuable information for practical survival estimations and relevant prognosticators in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who receive first line tyrosine kinase inhibitor.


暂无数据~

 V2
V2
